Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maruyama, Shuhei
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors 2022 (PHYSOR 2022) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/05
This paper proposes a new homogenization method, "Boundary Condition Free Homogenization (BCFH)". The traditional homogenization method separates the core calculation and the cell (assembly) calculation by assuming a specific boundary condition or a peripheral region in the cell calculation. Nevertheless, there are ambiguities and approximation in these assumptions, and they can also cause a decline in accuracy. BCFH aims to avoid these problems and improve the accuracy in the cell calculation such as homogenization. We imposed the conditions that the physical quantities in the cell related to the reaction rate preservation is preserved for any incoming partial current, during the homogenization. That is, the response matrices of cell average (or total) flux and outgoing partial current, to be the same form between heterogeneous and homogeneous system. As a result, homogenized parameters, such as cross-sections, superhomgenization factors, and discontinuity factors, are no longer dependent on a specific boundary condition. The new homogenized parameters obtained in this way are extended from the conventional vector form to the matrix form in BCFH. To investigate the performance of BCFH, numerical tests are done for the simplified models which originates in 750MW-class sodium-cooled fast reactor with MOX fuel core in Japan. It is found that BCFH is particularly effective in evaluating control rod reactivity worth and reaction rate distribution, compared to the traditional method. We conclude that the BCFH can be a promising homogenization concept for core neutronic analysis.
Wang, Z.; Duan, G.*; Matsunaga, Takuya*; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 157, p.119919_1 - 119919_20, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:77.06(Thermodynamics)Kondo, Hiroo*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Park, C. H.*; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 146(Part A), p.285 - 288, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)Herein, the wall shear stress in a double contraction nozzle has been evaluated experimentally to produce a liquid lithium (Li) target as a beam target for intense fusion neutron sources such as the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), the Advanced Fusion Neutron Source (A-FNS), and the DEMO Oriented Neutron Source (DONES). The boundary layer thickness and wall shear stress are essential physical parameters to understand erosion-corrosion by the high-speed liquid Li flow in the nozzle, which is the key component in producing a stable Li target. Therefore, these parameters were experimentally evaluated using an acrylic mock-up of the target assembly. The velocity distribution in the nozzle was measured by a laser-doppler velocimeter and the momentum thickness along the nozzle wall was calculated using an empirical prediction method. The resulting momentum thickness was used to estimate the variation of the wall shear stress along the nozzle wall. Consequently, the wall shear stress was at the maximum in the second convergent section in front of the nozzle exit.
Narukawa, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Jang, S.*; Amaya, Masaki
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM-14) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2018/09
Narukawa, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Jang, S.*; Amaya, Masaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 331, p.147 - 152, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shibamoto, Yasuteru
JAERI-Research 2005-016, 127 Pages, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Tian, R.; Nakajima, Norihiro; Yagawa, Genki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu, 10(1), p.397 - 400, 2005/05
An attempt is made to treat boundary conditions in EFGM through only nodal arrangements. One of major merits of the proposed nodal arrangement scheme is its straightforwardness in implementation. The accuracy of this nodal arrangement boundary treatment and its influence on convergence are assessed by comparing with the Lagrange multiplier and penalty methods using one- and two- dimensional problems. The nodal arrangement scheme shows a same performance as the Lagrange multiplier and penalty methods in the one-dimensional tests, but it evidently outperforms the penalty method in the two-dimensional tests.
Furuno, Akiko; Terada, Hiroaki; Chino, Masamichi; Yamazawa, Hiromi*
Atmospheric Environment, 38(40), p.6989 - 6998, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:41.46(Environmental Sciences)We have been developing the computer-based emergency response system WSPEEDI which predicts long-range atmospheric dispersion of radionuclides discharged into the atmosphere due to a nuclear accident. The first version of WSPEEDI has a shortage that the spatial and temporal variation of the atmospheric boundary layer was very simply parameterized. Therefore we have developed the new version accomplished with the atmospheric dynamic model, in which the turbulent diffusivity in the mixing layer is calculated with a turbulence closure model. This paper describes the results of performance evaluation of the new version of WSPEEDI by comparing the simulation results with the European Tracer Experiment data. As a result of the verification, it was shown that the increase in the horizontal resolution largely improved the accuracy of the model prediction. The use of the turbulence closure model instead of the simple parameterization largely contributed to improve reproducibility of horizontal distribution of plumes.
Shimizu, Akira; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Moriyama, Koichi*
JAERI-Tech 2004-051, 69 Pages, 2004/06
HTTR of JAERI will be connected with a hydrogen production system by steam reforming of methane for development of nuclear heat utilization technology. This facility will handle much inflammable gas near the nuclear reactor so that special safety consideration is necessary. This report describes the Probabilistic Safety Assessment (PSA) of inflammable gas leakage in the HTTR hydrogen production system. Vessels and pipes, which contain flammable gas, were divided into several systems. Probability of gas leakage were calculated at all candidate places. As a result of assessment, the counter measures such as double-covered inflammable gas pipes, small diameter instrument pipes, leakage detector and emergency shut off valves, are confirmed to be very effective to minimize the scale of explosion and to prevent the damage on nuclear plant.
 5 (012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary; A First-principles study
5 (012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary; A First-principles studyYamaguchi, Masatake; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kaburaki, Hideo
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 16(23), p.3933 - 3956, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:86 Percentile:92.94(Physics, Condensed Matter)A series of non-transition elements bound to the Ni  5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary (GB) and the (012) free surface (FS) systems has been studied by first-principles calculation using WIEN2k code. The multilayer relaxations in presence/absence of the solutes are determined by the force minimization. The binding energies at some GB/FS/bulk sites including both interstitial and substitutional sites are calculated for all the non-transition elements between
5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary (GB) and the (012) free surface (FS) systems has been studied by first-principles calculation using WIEN2k code. The multilayer relaxations in presence/absence of the solutes are determined by the force minimization. The binding energies at some GB/FS/bulk sites including both interstitial and substitutional sites are calculated for all the non-transition elements between  H and
H and 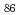 Rn. The GB/FS segregation energy is obtained by calculating the binding energy difference between the GB/FS site and the bulk site. The embrittling potency energy is obtained by calculating the difference between the GB and FS segregation energies based on Rice-Wang model. Our results show that most of the non-transition elements have negative GB/FS segregation energies. Here, this means that there exists a segregation site in the GB/FS. The embrittling potency energies are positive for most of the solutes. However, some exceptions like Be, B, C, and Si having negative and large embrittling potency can enhance the GB cohesion. Our results are found to be consistent with the experimental findings.
Rn. The GB/FS segregation energy is obtained by calculating the binding energy difference between the GB/FS site and the bulk site. The embrittling potency energy is obtained by calculating the difference between the GB and FS segregation energies based on Rice-Wang model. Our results show that most of the non-transition elements have negative GB/FS segregation energies. Here, this means that there exists a segregation site in the GB/FS. The embrittling potency energies are positive for most of the solutes. However, some exceptions like Be, B, C, and Si having negative and large embrittling potency can enhance the GB cohesion. Our results are found to be consistent with the experimental findings.
Hoshiya, Taiji*; Takaya, Shigeru*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Nagae, Yuji*; Miwa, Yukio; Abe, Yasuhiro*; Omi, Masao; Tsukada, Takashi; Aoto, Kazumi*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 29(4), p.1687 - 1690, 2004/06
JAERI and JNC have begun the cooperative research of evaluation techniques of structural material degradation in FBR and LWR, which based on magnetic and corrosion properties along grain boundaries. Magnetic method has been proposed as the one of the non-destructive detection techniques on the early stage of creep-damage before crack initiation for aged structural materials of FBRs. The effects of applied stress on natural magnetization were investigated on paramagnetic stainless steels having creep-damages. On the other hand, corrosion properties and magneto-optical characteristics of ion-irradiated stainless steels in the vicinity of grain boundaries were estimated by AFM and Kerr effect microscope, respectively. These degradations were induced by changes in characteristics in the vicinity of grain boundaries. It is found that the initial level of progressing process of damage can detect changes in magnetic and corrosion properties along grain boundaries of aged and degraded nuclear plants structural materials.
Terada, Hiroaki; Furuno, Akiko; Chino, Masamichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(5), p.632 - 640, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:79.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)The new version of WSPEEDI (Worldwide version of System for Prediction of Environmental Emergency Dose Information) is developed by introducing the combination of models, the atmospheric dynamic model MM5 and the Lagrangian particle dispersion model GEARN-new to improve the prediction capability. One of the improvements by the new system is that Environmental contaminations in multi domains are predicted simultaneously, and the other is that more precise physical processes are considered by using predicted meteorological conditions with high resolution in time and space. The performance of the system is evaluated for the test calculations of hypothetical nuclear accident in the East Asia region and the Chernobyl accident. The results of test calculation in East Asia seem to be reasonable and the calculated surface air concentrations of  Cs from Chernobyl show good agreement with measurements.
Cs from Chernobyl show good agreement with measurements.
Shimada, Michiya
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(3), p.222 - 226, 2004/03
Discussion is made on objectives of edge plasma and plasma-wall interaction studies, divertor performance projection of ITER and key R&D issues on plasma-wall interaction including material issues, tritium retention, and transient events like ELMs and disruptions. A perspective of future development is discussed for the purpose of projection to and control of ITER plasma.
 dinger equation
dinger equationUtsumi, Takayuki*; Yabe, Takashi*; Koga, J. K.; Aoki, Takayuki*; Sekine, Masatoshi*
Computer Physics Communications, 157(2), p.121 - 138, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:51.51(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)no abstracts in English
 5(012) tilt grain boundary
5(012) tilt grain boundaryYamaguchi, Masatake; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kaburaki, Hideo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73(2), p.441 - 449, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:71.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The electronic structures of  5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary (GB) and (012) free surface (FS) systems for nickel including hydrogen are calculated by the full-potential linearized augmented plane wave method with the generalized gradient approximation. The difference of the binding energies between the
5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary (GB) and (012) free surface (FS) systems for nickel including hydrogen are calculated by the full-potential linearized augmented plane wave method with the generalized gradient approximation. The difference of the binding energies between the  5(012)GB/FS site and the inner bulk site is obtained as the GB/FS segregation energy, and the difference between GB and FS segregation energies as the embrittling potency energy. The segregation position of hydrogen atom is determined by the force minimization. We find that hydrogen atom prefers
5(012)GB/FS site and the inner bulk site is obtained as the GB/FS segregation energy, and the difference between GB and FS segregation energies as the embrittling potency energy. The segregation position of hydrogen atom is determined by the force minimization. We find that hydrogen atom prefers  5(012)GB to inner bulk energetically by about 0.3 eV/H, while it prefers (012)FS to the GB by about 0.3-0.4 eV/H. The open space at GB may be occupied by an additional interstitial Ni atom since it increases the GB energy by only about 10%. In this case, the GB segregation energy of hydrogen reduces, which makes the segregation difficult. The calculated zero-point energies of hydrogen at inner bulk, GB, and FS sites are within 0.12-0.16eV/H.
5(012)GB to inner bulk energetically by about 0.3 eV/H, while it prefers (012)FS to the GB by about 0.3-0.4 eV/H. The open space at GB may be occupied by an additional interstitial Ni atom since it increases the GB energy by only about 10%. In this case, the GB segregation energy of hydrogen reduces, which makes the segregation difficult. The calculated zero-point energies of hydrogen at inner bulk, GB, and FS sites are within 0.12-0.16eV/H.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsukada, Takashi; Tsuji, Hirokazu
JAERI-Conf 2003-001, p.397 - 404, 2003/03
It is essential to evaluate corrosion behavior at grain boundary of irradiated materials for mechanistic understanding of Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC). However there is no suitable technique to evaluate grain boundary corrosion behavior of irradiated materials. The aim of this work is to develop the measurement method for the grain boundary corrosion behavior of irradiated materials using atomic force microscope (AFM). Ni ion was irradiated to solution annealed Fe-18Cr-12Ni alloy at about 573K. The peak damage level was estimated as 1 dpa. To study relationship of grain boundary character and corrosion behavior, orientation imaging microscope (OIM) observation was conducted. After potentiostatic corrosion procedure, the surface of the specimens were examined with AFM and OIM. Some of grain boundaries were corroded, and these were random coincidence grain boundaries. The depth of the corroded region at grain boundaries was successfully evaluated with AFM in nanometer scale.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi
Dai-12-Kai MAGDA Konfarensu (Oita) Koen Rombunshu, p.191 - 196, 2003/00
Development and research about analytical method for the study of corrosion behavior of austenitic stainless steel after irradiation was conducted from the point of view for basic study of IASCC (Irradiation Assisted Stress Corrosion Cracking). Ion irradiations were conducted with several irradiation conditions these were irradiation temperature, radiation damage, the contents of helium (He) implantation. AFM (Atomic Force Microscope) was used to evaluate surface condition of irradiated specimens after corrosion procedure. Corrosion condition was developed to obtain good surface condition of irradiated specimens to evaluate corrosion behavior by AFM. It was succeeded and corrosion behavior at inside of grains and grain boundaries of irradiated specimens was obtained. EBSP (Electron Backscatter Diffraction Pattern) was used to evaluate relation of corrosion behavior with grain boundary character. Moreover, relations of corrosion behavior with irradiation condition were discussed.
Fujimura, Toichiro*; Okumura, Keisuke
JAERI-Research 2002-024, 27 Pages, 2002/11
A prototype version of a diffusion code has been developed to analyze the hexagonal core as reduced moderation reactor and the applicability of some acceleration methods have been investigated to accelerate the convergence of the iterative solution method. The hexagonal core is divided into regular triangular prisms in the three-dimensional code MOSRA-Prism and a polynomial expansion nodal method is applied to approximate the neutron flux distribution by a cubic polynomial. The multi-group diffusion equation is solved iteratively with ordinal inner and outer iterations and the effectiveness of acceleration methods is ascertained by applying an adaptive acceleration method and a neutron source extrapolation method, respectively. The formulation of the polynomial expansion nodal method is outlined in the report and the local and global effectiveness of the acceleration methods is discussed with various sample calculations. A new general expression of vacuum boundary condition, derived in the formulation is also described.
Tokuda, Shinji
Theory of Fusion Plasmas, p.87 - 102, 2002/00
We report on recent development of solution methods of the Newcomb equation and boundary layer equations, which play important roles in MHD stability analysis of a tokamak. Especially, the two-dimensional Newcomb equation is applied to external modes and the method is desctribed for computing the stability matrix of the external modes.
 O+SO
O+SO atmosphere
atmosphereKurata, Yuji; Suzuki, Tomio; Shimizu, Saburo
JAERI-Research 2000-011, p.56 - 0, 2000/03
no abstracts in English